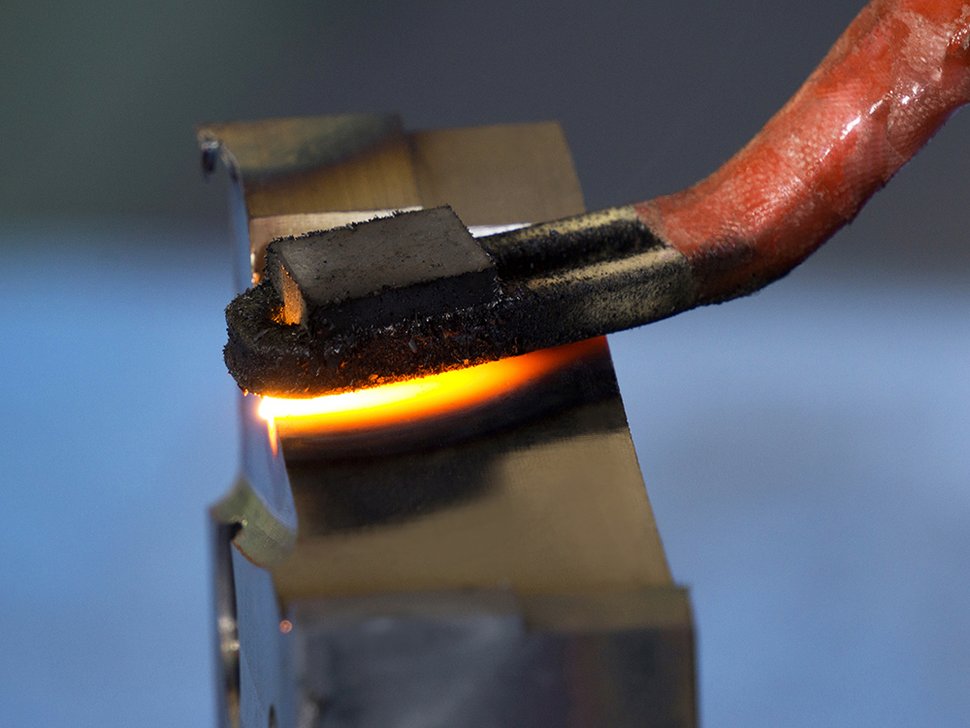
Cutting edge hardening
Full hardness for toolmaking: Cutting edge hardening plays an important role in toolmaking and especially in sheet metal processing. The process is used to precisely harden those tool details that are subject to particularly high loads in a punch-press or progression tool. To do this, users heat the outermost layer of the cutting edge to a temperature of approx. 800 to 900 degrees Celsius. This can be done manually or automatically. After cooling, the cutting-edge surface layer is hard and wear resistant.

